Bluetooth Or Wifi Faster
-

Here's why you should use 5. GHz Wi. Fi instead of 2. GHz. While this could be the case in certain situations, there are many reasons why (from a technical perspective) 5. GHz Wi. Fi may perform better than 2. GHz Wi. Fi; similarly, there are reasons why 2.
GHz Wi. Fi may work better for you than 5. GHz Wi. Fi. The differences are very much specific to the environment in which each network is being used.
Updated May 2. 6, 2. Way back when Wi- Fi first came out, there were two versions that you could chose from: 8. From a consumer perspective, there wasn’t much difference between the two. Devices based on 8.
GHz spectrum. These days, it’s getting pretty crowded, and to help address the digital noise that comes with it, 5. GHz Wi. Fi is making a comeback. GHz Wi. Fi)8. 02. It was built around the 5.
Bluetooth technology allows two devices near each other to communicate at a maximum speed of 3 Mb per second. In the grand scheme of wireless communication, Bluetooth. Wifi will be faster than Bluetooth in almost every case. Even the oldest wifi standard, a, has speeds up to 54 Mbps while the most common Bluetooth standard. Bluetooth 4.0 transfers data with speeds up to 25 Mbps. Compare this to the Wi-Fi Direct setup, which promises data transfer at speeds of 250 Mbps. WiFi Speed really slow while Bluetooth is on. My usual WiFi speed on my room is 10mbps, when using the bluetooth jumps down to 0.50mbps which is insane.

GHz spectrum, but failed to gain much traction in the consumer market. Being the “first” Wi- Fi protocol, it faced a steep learning curve and deployment problems which delayed the deployment of 8.

The wireless standard's Special Interest Group has officially adopted the Bluetooth 5 spec, clearing. Faster Bluetooth 3.0 Launches with WiFi Twist The Bluetooth Special Interest Group Tuesday officially launched Bluetooth 3.0 with some big claims for the short-range.
Also, at the time, components that operated on 5. GHz were generally more expensive and harder to come by than 2.
GHz components. 8. GHz Wi. Fi)When 8. It offered basically the same features as 8. Due to these factors, 8. Popularity of Wi- Fi began to grow, and the standards that backed it continued to improve. GHz Wi. Fi)By 2. 00. This version of the Wi- Fi standard brought some of 8.
All together the changes were able to increase speeds up to 5. Mbps. Thanks to backwards- compatibility with devices that used 8. When this article was orginally written, 8.
Wi- Fi available. Today it’s still a viable option, but is giving way to 8. Unfortunately, 8.
How Fast Is Bluetooth
Bluetooth Or Wifi Faster Than Wired
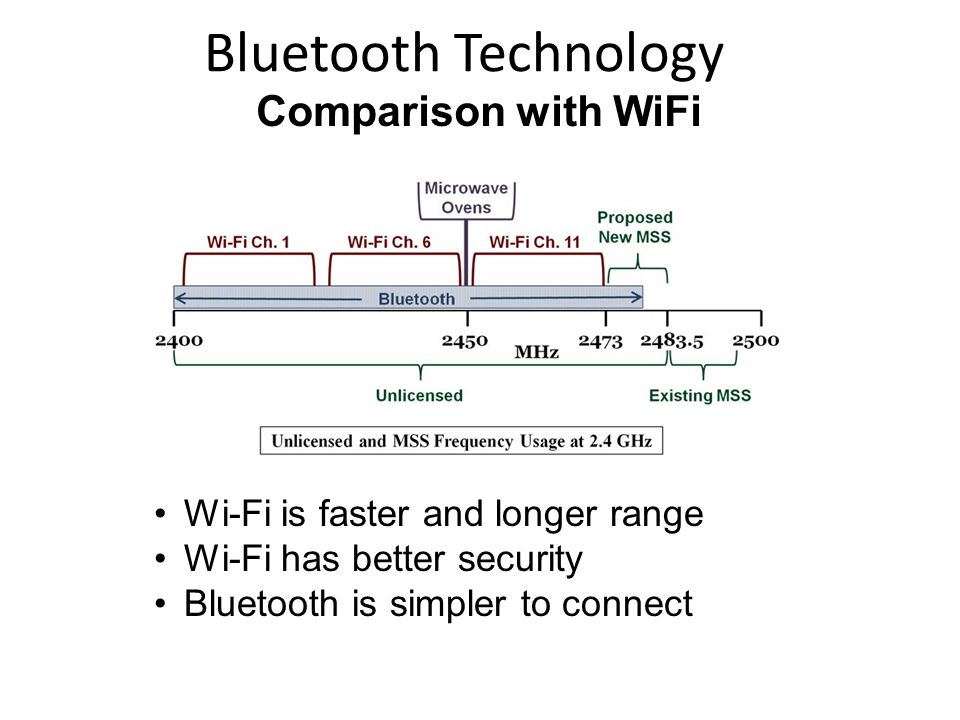
GHz spectrum, which, as you might have suspected, is getting pretty crowded since all those Wi- Fi devices operate on the same frequency. Bluetooth, Microwaves, & Wireless Peripherals (2. GHz)Almost everyone has a microwave in their house.
Some of them emit some of the radiation used to warm up your pizza outside of the unit. No, it’s not supposed to do that, but some do, especially as they get older and components start to break down. In addition to being harmful to your health, their “spurious emissions” cause bursts of noise around the 2.
GHz spectrum that can severely interfere with your wireless signal. If you find that you’re in this situation, you might want to replace your microwave oven! Bluetooth used to be limited to headsets and other special- use equipment, but as its feature- set increased, devices using Bluetooth increased too — and not just in number, but in the bandwidth they use and the amount of time they’re turned on. Bluetooth speakers and docks are a good example of this, though wearables are quickly becoming more commonplace as well. Wireless keyboards, mice, trackpads, and trackballs can use Bluetooth to connect. Even those that use their own proprietary wireless hardware are typically still using the 2.
- Also like WiFi, Bluetooth is “fairly” secure.
- But Bluetooth Interference from other devices can be frustrating. Here are solutions.
- The Question. SuperUser reader jt0dd wants to know if Bluetooth is faster than Wi-Fi: I notice that on my iPhone, when I use my personal hot-spot to distribute Wi-Fi.

GHz spectrum. 8. 02. GHz or 5. GHz Wi. Fi)When 8. 02. 1.
Mbps. What’s more, 8. GHz or 5. Ghz spectra. Like the other standards before it, 8. Unfortunately, since most devices already on the market were already using 2. GHz, most 8. 02. 1.
GHz as the primary operating frequency, and some devices didn’t even include the hardware to use 5. Ghz at all. Some let you pick between 2. GHz and 5. GHz operation (but usually not both), but since most people still had some 2. GHz devices they kept their networks on 2. GHz rather than making the switch across the board. GHz Wi. Fi)8. 02. January 2. 01. 4, but devices based on the draft specification were available for months prior.
This standard brings the maximum data rates up to 1. Gbps (almost double that of 8. In most 8. 02. 1. GHz and 5. GHz hardware is included, though most segregate the traffic from each onto its own network. Advantages of 5. GHz Wi. Fi. Finally users can take advantage of the reduced noise available in the 5. GHz spectrum. This generally provides faster data rates, fewer disconnects, and a more enjoyable experience.
Microwaves don’t operate up there (not even newer ones), so that source of noise is eliminated, too. There are many more reasons why 8. GHz spectrum, rather than about 8.
With a compatible router or WAP, your 8. With a stronger the signal and faster the throughput, less power is required to get your signal above the noise floor, which should result in better battery life in addition to better network performance. GHz Wi. Fi Considerations. Not all of your devices are going to have 5. GHz compatibility built- in, they will still work every bit as well as they did before on 2.
GHz, but should work even better once you offload traffic from that network onto your 5. GHz network. There are some potential disadvantages to 5. GHz though. If two signals are transmitted using the same power and equivalent antennas, the signal with the higher frequency will travel a shorter distance – in other words (all things being equal), 5. GHz won’t travel as far as 2. GHz. Since the data may not travel as far over 5. GHz, you may not have as much interference from neighbors as you would have on 2.
GHz. Then again, neither will your neighbors’ (which could very well be a major advantage to both you and them). Other environmental factors also play into whether 5. GHz will be better for your circumstances. A country home with relatively few devices and neighbors who live 1/4 mile away may benefit from 2. GHz over 5. GHz. A suburban home with neighbors within arm’s length of each other may benefit from 5. GHz rather than 2. GHz. Just as physical obstacles can prevent you from passing from one room to another (walls, for example), obstacles can block, reduce, or reflect signals, too.
The frequency of the signal (in this case 2. GHz versus 5. GHz) comes into play, as does the composition of the walls. Brick, drywall, plaster, glass, and steel all have different properties, and signals on one frequency may travel through them better than signals on another frequency.
It all depends on the environment in which your network is deployed. All in all, I’d highly recommend that you upgrade your router or WAP to 8. GHz and 5. GHz networks, then move as much of your wireless traffic to the 5. GHz side as possible.
You’ll have less noise, less interference, better speeds, a more stable connection, and possibly even better battery life. What more could you want?



/https%3A%2F%2Fassets.over-blog.com%2Ft%2Fcedistic%2Fcamera.png)